Mechanisms of the human heart
Rhoda King • 2025-01-17
The human heart is composed of a variety of different muscles that helps it performs its crucial functions of supplying oxygen rich blood around the body.
The heart beats around 100,000 times each day continuously pumps about five litres of blood around the body through a network of blood arteries and veins in the circulatory system.
The blood pumped would delivers oxygen and nutrients to all the different parts of the body to help our organs and muscles work. Our blood also filters away unwanted carbon dioxide and waste products, vital to prevent any infections the wastes would cause.
Our heart has four major areas. It has a left side, and a right side separated by a muscular wall called the septum. Both sides have an upper chamber and lower chamber:
The two upper chambers are called the left atrium and the right atrium they receive blood flowing into the heart, the two lower chambers are called the left ventricle and the right ventricle, they pump blood out of the heart.[i]
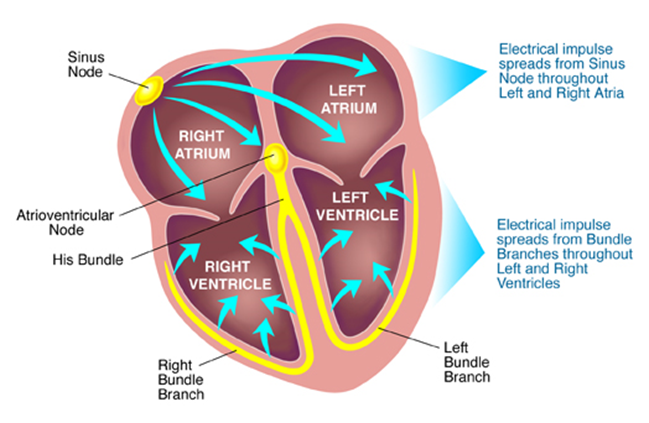
The electrical conduction system of the heart
The beating of the heart is myogenic, which means it beats without any external stimulus. The sinoatrial node is a group of cells in the wall of the right atrium. The SAN starts a wave of excitation, and this makes the atria contract.
The Annulus fibrosus, which is a region of non-conducting tissue prevents the excitation from spreading straight to the ventricles so, the wave of excitation is carried to the atrioventricular node (AVN).
After a slight delay, the AVN is stimulated and passes the stimulation along the bundle of His. This delay means ensures that the ventricles contract after the atria.
The bundle of His is a collection of conducting tissue in the septum. It divides into two conducting fibres, called Purkyne tissue, and carries the wave of excitation along them.
The Purkyne fibres are situated around the ventricles and start the depolarisation of the ventricles from the bottom of the heart. This causes the ventricles to contract and blood is pushed out of the pulmonary artery and aorta. [i]
Figure one - a diagram of the human heart with relation to electrical impulses Coronary heart diseases
Coronary heart disease is the medical term that describes what happens when our blood is blocked or intercepted by a build-up of fatty substances in the coronary arteries. Over time, the walls of the arteries can become bulked up with fatty deposits. It can be caused by lifestyle factors, such as smoking, bad diets, drinking excessive amounts of alcohol etc. There is a risk of getting coronary heart diseases if you have conditions such as a high blood pressure, cholesterol, or diabetes.
Although Coronary heart disease cannot be cured, there are certain treatments that can help manage the symptoms and reduce the chances of problems such as heart attacks.
Treatment can include:
- lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and avoiding smoking.
- medicines
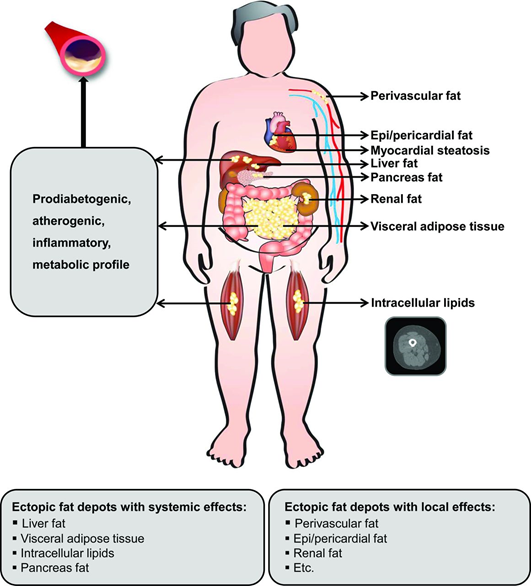
- surgery Visceral fat is a type of body that is deep within the walls in the abdomen surrounding the internal organs. Some levels of visceral fat are healthy and help protect the organs. However, too much visceral fat is dangerous for our health. Visceral fat is also known as active fat, and it plays an active role in how the body works. Excessive visceral fat can lead to serious health issues such as diabetes, heart disease and strokes
Genetic and external factors decide the amount of visceral fat you can accumulate. Genetics decide your body shape and how your body stores visceral fat but environmental factors such as activity levels, diet and exercise also have a significant role. A poor diet high in fatty foods and sugars and an inactive daily routine sets up the body for an increase in visceral fat. stress is also an important factor too. it activates a hormone in the body called cortisol. cortisol activates your body’s “fight-or-flight” response, which triggers the storage of more visceral fat.[ii]
Figure two - a diagram of the human body with varieties of fats/lipids
Biodegradable Nano Robots for Targeted TNF – An Inhibition in Visceral Fat Reduction.
“Tumour Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF alpha), is an inflammatory cytokine produced by macrophages/monocytes during acute inflammation and manages a diverse range of signalling events within cells, leading to necrosis or apoptosis. The protein is also important for resistance to infection and cancers”.[i]
TNF-alpha is a protein, cytokine to be exact, which is a type of signalling protein involve in immune responses and inflammation and is considered as one of deciding factors of insulin resistance. However, several data suggest that TNF-alpha expression itself, could be modulated by the degree of plasma insulin levels. In order to really find out what causes the increase of plasma TNF-alpha levels in type 2 diabetes, a study was made on the impact of intensive insulin treatment on plasma TNF-alpha levels on 16 type 2 diabetic subjects with failure to oral antidiabetic medication.
Furthermore, there was an analysis on the relationship between plasma TNF-alpha levels and total regional body fat measurements using anthropometry, bioenergetics absorptiometry and computed tomography in a cohort of 33 Caucasian obese type 2 diabetic subjects (BMI: 32.2 +/- 4.4 kg/m (2)).
The plasma TNF-alpha level was neither affected by plasma glucose level variations nor intensive insulin treatment despite a 37 % decrease in daily insulin needs at the end of insulin therapy (total duration: 11.5 +/- 2.0 days). The plasma TNF-alpha level was similar in adults and unrelated to age, fasting glycemia or HbA1c. A relationship was highlighted with BMI (r =0.39, p <0.02), but not with total fat mass. This relationship was only dependent on the intra-abdominal fat mass amount as assessed by the waist-to-hip circumference ratio (r =0.52, p <0.01) and the visceral adipose tissue area (r =0.56, p <0. 01). These results show that plasma TNF-alpha levels are essentially dependent on visceral fat amount, thus suggesting that TNF-alpha could be one of the factors mediating insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk in obese type 2 diabetic patients. [ii]
Epicardial fat is considered a type of visceral fat although visceral fat is genuinely stored deep inside the abdomen surrounding certain organs like the liver and intestines, epicardial fats is specifically the fat that is accumulated around the heart is located between the hearts outer lining and the muscle itself and it shares as many of the risks that's a visceral fact form including information and resistance to insulin bays also metabolically active and it can secrete inflammatory substances that can contribute to cardiovascular diseases. “It is also associated with other known factors, such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, age and hypertension, which makes the interpretation of its role as an independent risk marker intricate” [iii].
I propose an innovative approach to targeting and treating visceral fat inflammation by using a biodegradable nano robot, “RN-X” the grafted with self-antigen cells.
RN-X will be designed to detect to detect TNF alpha and upon detection release a “therapeutic agent” the “RK-187” to inhibit TNF activity, thus limiting those harmful effects of visceral fat accumulation.
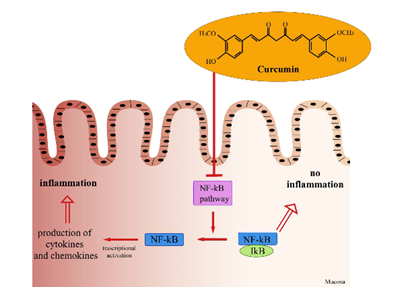
The RK-187 would be my theoretical biological agent, and it works almost as an enzyme inhibitor by binding to the TNF A and it blocks it from binding with receptors in the cells of the body. Curcumin is a compound that is found in turmeric, and it is known for its wonderful ability to fight inflammation, although inflammation is a natural process in the body when it is left out of control it can lead to serious health problems like heart diseases and arthritis. Curcumin can help reduce the amount of TNF alpha in the body.[iv]
Now imagine if we could create a drug that combines curcumins ability to fight inflammation with the power of medications that can directly block TNF alpha. These TNF alpha blockers are already used in medicine to treat diseases like arthritis and Crohn’s disease but they have a side effects, Combining curcumin with TNF alpha blockers could potentially give rise to a drug that is more natural and has fewer side effects and works in a new way to combat epicardial fats.
The main concept behind my approach is the creation of a robot that is capable to enter the bloodstream and potentially into the heart and it will be able to detect harmful fats in the body that hold TNF-A proteins. The RN-X in theory will be made using biodegradable materials that can dissolve easily in the bloodstream and would not cause any harm and the most obvious choice that came into mind to use would be collagen, because it can which can naturally decompose and is compatible with the human tissue.
Additionally, RN-X will be grafted with the body's own self antigens and this feature would ensure that the n RN-X would remain invisible to the immune system so that immune system would not tigger an attack when it recognises it as a foreign object.
The first step of the RN-X involves the robots detecting the presence of inflammatory marker which would be the TNF-A in the visible visceral fat.
The RK-187 are released in response to chronic inflammation which is an indicator of excessive visceral fat. My RN-X will be embedded with bioreceptors which are the specialised molecules designed to bind with TFA or other markets and once the receptors come into contact with elevated levels of TNF-A it will be stimulated to release the “therapeutic theoretical drug”( the RW-20) that would be mean primarily consistent of RK-187at the site of the visceral fat.
By delivering the RK-187 directly to the inflamed tissue the RN-X will reduce the inflammatory response tissues and reduce the size of visceral fat deposits and prevent damage to the surrounding tissues .The biodegradability of the n RN-X allows for the continued release of embryo overtime as the RN-X degrades, it can also release tiny amounts of the” RK-187 in such a way that mimics natural tissue processes.
References
https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/how-a-healthy-heart-works
[1] https://www.savemyexams.com/a-level/biology/ocr/17/revision-notes/3-exchange--transport/3-2-transport-in-animals/3-2-9-heart-action-initiation--control/
[1] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronary-heart-disease/#overview
[1] https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24147-visceral-fat
[1] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10891884/#:~:text=Tumour%20Necrosis%20Factor%20alpha%20(TNF,resistance%20to%20infection%20and%20cancers.
[1] Bertin E, Nguyen P, Guenounou M, Durlach V, Potron G, Leutenegger M. Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) are essentially dependent on visceral fat amount in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. 2000 May;26(3):178-82. PMID: 10880890.
See More Posts
Copyright © 2021 Govest, Inc. All rights reserved.